
레버리지비율
레버리지비율은 ‘기본자본(Tier 1) / 총익스포저(난외자산 포함) × 100’으로 정의된다. 분자의 자본은 바젤Ⅲ 기준 기본자본(Tier 1)을 사용하며 분모의 총익스포저는 위험가중 자산 기반의 자기자본비율과 달리 명목가액을 기준으로 하여 산출한다. 자기자본비율 규제 하에서 은행은 호황기에 보유자산의 위험가중치를 낮게 설정함으로써 외형상 높은 자기자본 수준을 유지하면서 레버리지를 확대할 수 있었다. 이 경우 위기 발생시 급격한 디레버리징(자산처분, 부채상환)이 발생하여 위기가 증폭되는 악순환이 발생할 수 있는 데, 레버리지비율 규제는 이러한 자기자본비율 규제의 문제점을 보완한다고 할 수 있다. 바젤은행감독위원회(BCBS)는 2015년 1월부터 레버리지비율 공시를 의무화하였으며 은행들은 2018년 1월부터 최저 레버리지비율(3%)도 준수해야 한다. 이 밖에도 글로벌 시스템적 중요 은행(G-SIB)에는 2022년 1월부터 시스템적 중요도에 따라 추가 레버리지 비율이 부과될 예정이다. 이는 위험가중자산 기반 자기자본비율 규제에서 G-SIB에 대해 부과하고 있는 추가자본 규제와의 일관성을 갖추기 위한 것으로 G-SIB은 자기자본비율 규제상 부과되는 추가자본의 50%만큼 상향 조정된 레버리지비율을 준수해야 한다. 예컨대 2%의 추가자본이 부과된 G-SIB이 준수해야 할 레버리지비율은 최저 레버리지비율 3%에 추가자본의 50%에 해당하는 1%가 가산된 4%가 된다. 동 레버리지비율을 준수하 지 못하는 경우 이익처분이 제한되는 것은 G-SIB 추가자본의 미준수시와 동일하다.
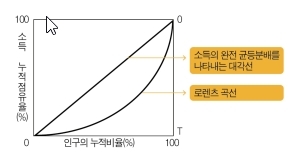
로렌츠곡선
1905년 미국의 통계학자인 로렌츠(M. Lorenz)가 소득의 불평등 정도를 측정하기 위해 제안한 것으로, 인구의 누적비율을 가로축에 소득의 누적점유율을 세로축에 놓고 이들의 관계를 그림으로 표시한 곡선을 말한다. 모든 사람의 소득이 일정하다면 인구가 누적되어도 소득 누적액이 일정할 것이므로 로렌츠 곡선(Lorenz Curve)은 아래 그림의 OO′선과 같은 대각선이 된다. 반면 소득이 불평등하다면 처음에는 소득이 적은 사람들의 누적액이 더해져 그래프의 기울기가 완만하다가 뒤로 갈수록 소득이 많은 사람들의 누적액이 더해지면서 가파른 모양의 아래로 늘어진 곡선이 되며, 한 사람이 모든 소득을 다 가지고 있는 경우에는 OTO′선과 같은 모양이 된다. 따라서 로렌츠 곡선이 OO′선에 가까워질수록 분배상태가 평등하고, OTO′선에 가까워질수록 불평등 정도가 높다고 판단할 수 있다. 로렌츠 곡선은 한 나라의 소득분배 상태를 그림으로 볼 수 있다는 장점이 있으나 그 정도를 정량적으로 표시할 수 없다는 단점이 있는데, 소득분배 상태를 정량적으로 파악하기 위해서는 지니계수를 이용하여야 한다. 지니계수는 아래 그림의 대각선과 로렌츠곡선 사이의 면적을 대각선 아래 삼각형 면적 전체로 나눈 것으로, 소득분배가 완전히 평등하다면 대각선과 로렌츠곡선 사이의 면적이 0이 되어 지니계수는 0이 된다. 반대로 소득분배가 완전히 불평등하다면 대각선과 로렌츠곡선 아래의 면적이 대각선 아래 전체 면적과 같게 되므로 지니계수는 1이 된다.

로보어드바이저
로보어드바이저(robo-advisor)는 로봇(robot)과 자문가(advisor)의 합성어이다. 이는 인공지능 알고리즘, 빅데이터 등을 활용하여 투자자의 투자성향 리스크선호도 목표수 익률 등을 분석하고 그 결과를 바탕으로 투자자문 자산운용 등 온라인 자산관리서비스 를 제공하는 것이다. 서비스 제공 과정에서 비용으로 작용하는 사람의 개입을 최소화함 으로써 기존 자산관리서비스보다 더 낮은 최소투자금액과 더 싼 수수료로 소액 자산을 가진 일반 개인도 더 쉽게 접근할 수 있게 되었다. 로보어드바이저 서비스는 금융회사의 자문 또는 운용인력이 로보어드바이저의 자산배분 결과를 활용하여 고객에게 자문(자문 형)하거나 고객 자산을 직접 운용(일임형)하는 형태나, 로보어드바이저가 고객에게 자문 하거나 고객 자산을 직접 운용하는 형태로 이뤄진다. 로보어드바이저 시장에서는 미국이 가장 앞서 나가고 있다. 우리나라의 경우 2021년 3월 현재, 코스콤(KOSCOM)의 테스트 베드센터 심사를 통과한 14군데의 금융기관(은행, 증권사 및 투자자문사 등)이 로보어드 바이저 서비스를 제공하고 있다.
Leverage ratio
The leverage ratio is defined as 'basic capital (Tier 1) / total exposure (including out-of-the-box assets) × 100'. The capital of the molecule uses the basic capital (Tier 1) based on Basel III, and the total exposure of the denominator is calculated based on the nominal value, unlike the risk-weighted asset-based equity capital ratio. Under the regulation of the equity capital ratio, banks were able to expand leverage while maintaining a high level of equity capital by setting a low risk weight for their assets during the boom. In this case, rapid deleveraging (asset disposal, debt repayment) may occur in the event of a crisis, resulting in a vicious cycle in which the crisis is amplified, and the leverage ratio regulation compensates for the problem of regulating the equity capital ratio. The Basel Committee on Banking Supervision (BCBS) has mandated disclosure of the leverage ratio since January 2015, and banks must also comply with the minimum leverage ratio (3%) from January 2018. In addition, additional leverage rates will be imposed on the Global Systemic Important Banks (G-SIBs) from January 2022 depending on their systematic importance. This is to be consistent with the additional capital regulation imposed on the G-SIB in the risk-weighted asset-based equity ratio regulation, which must comply with the leverage ratio raised by 50% of the additional capital imposed by the equity ratio regulation. For example, the leverage ratio to be observed by the G-SIB, which is imposed with an additional capital of 2%, is 4% which is the minimum leverage ratio of 3% and 1% which is 50% of the additional capital. If the leverage ratio is not complied with, the restriction on the disposition of profits is the same as if the G-SIB additional capital is not complied with.
Lorentz curve
It was proposed by American statistician M. Lorenz in 1905 to measure the degree of income inequality, and refers to a curve in which the cumulative ratio of the population is placed on the horizontal axis and the cumulative share of income is placed on the vertical axis. If everyone's income is constant, the accumulated amount of income will be constant even if the population is accumulated, so the Lorenz curve becomes a diagonal line as shown in the figure below. On the other hand, if income is unequal, the slope of the graph is gentle at first due to the accumulation of low-income people, and then the accumulation of high-income people is added to form a steep curve, and if one has all income, it is the same shape as the OTO' line. Therefore, it can be judged that the closer the Lorentz curve approaches the OO′ line, the more equal the distribution state, and the higher the degree of inequality is. The Lorentz curve has the advantage of being able to see a country's income distribution status as a picture, but it has the disadvantage of not being able to quantitatively display the degree, and the Gini coefficient must be used to quantitatively grasp the income distribution status. The Gini coefficient is the area between the diagonal and Lorentz curves in the figure below divided by the entire area of the triangle below the diagonal, and if the income distribution is completely equal, the area between the diagonal and Lorentz curves becomes 0. Conversely, if the income distribution is completely unequal, the area under the diagonal and Lorentz curves will be equal to the total area under the diagonal, so the Gini coefficient will be 1.
RoboAdvisor
Robo-advisor is a combination of robot and advisor. This analyzes investors' investment propensity risk preference target return using artificial intelligence algorithms and big data, and provides online asset management services such as investment advisory asset management based on the results. By minimizing the intervention of people acting as costs in the service provision process, it has become easier for ordinary individuals with small assets to access with a lower minimum investment amount and lower fees than existing asset management services. The RoboAdvisor service consists of consulting or operating personnel of financial companies using the results of the RoboAdvisor's asset allocation to advise customers (advisory type) or direct management of customer assets. The U.S. is leading the robo-advisor market. In Korea, as of March 2021, 14 financial institutions (banks, securities firms, investment advisors, etc.) that have passed KOSCOM's test bed center screening are providing RoboAdvisor services.
'경제금융용어' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 마이크로 크레디트,마찰적 실업,만기수익률 (0) | 2023.09.14 |
|---|---|
| 리디노미네이션,마샬의 k,마스트리히트조약 (0) | 2023.09.13 |
| 래퍼곡선,레그테크,레버리지 효과 (0) | 2023.09.13 |
| 디스인플레이션,디커플링/커플링,디플레이션 (2) | 2023.09.12 |
| 듀레이션,등록발행,디레버리징 (0) | 2023.09.12 |




